In this article we will learn about Wildcard Route in Angular. This is a continuation part of our previous article where we discussed Redirect Routes in Angular. At the end of this article, you will understand what exactly Wildcard Route is and when and how to use Wildcard Route in Angular Application. You can also find detailed information about routing in my previous article Routing in Angular.
What is Wildcard Route in Angular?
In Angular Application, the Wildcard Route is used to handle invalid URLs. If a user enters an invalid URL or if you delete an existing URL from your application, the 404 page not found error page is displayed by default. In such cases, instead of displaying the default error page, show a custom error page, which is possible with the Angular Wildcard Route.
How to use Wildcard Route in Angular?
A Wildcard route has a path consisting of two asterisks (**). It matches every URL, the router will select this route if it can’t match a route earlier in the configuration. A Wildcard Route can navigate to a custom component or can redirect to an existing route. The syntax to use Wildcard Route is given below.
We have the route link setup as the above, when we search the Invalid URL it call the NotFoundComponenet like below,
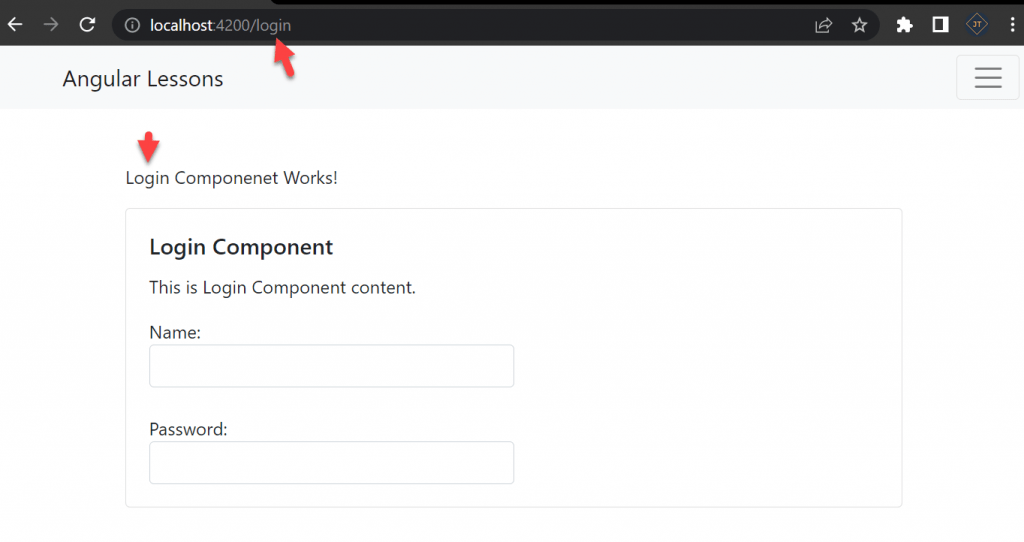
On below you can see when we navigate to Login route then the Login component is called.
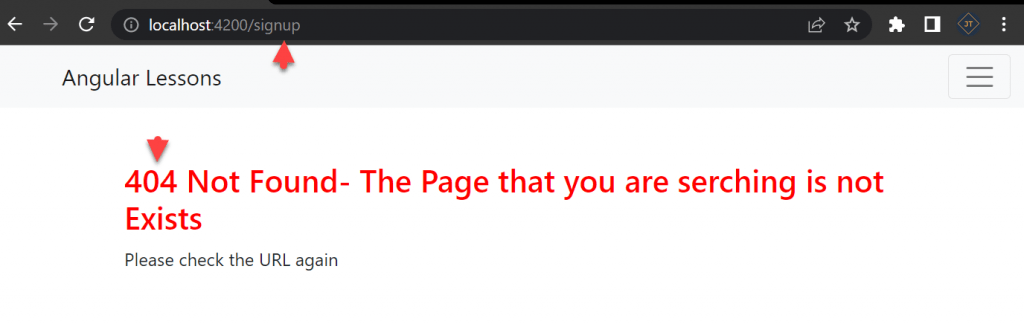
But you can see we call the route here /signup that doesn’t exist our route component, then it navigate to the NotFoundComponent like below.
What should be the Order of Angular Routes?
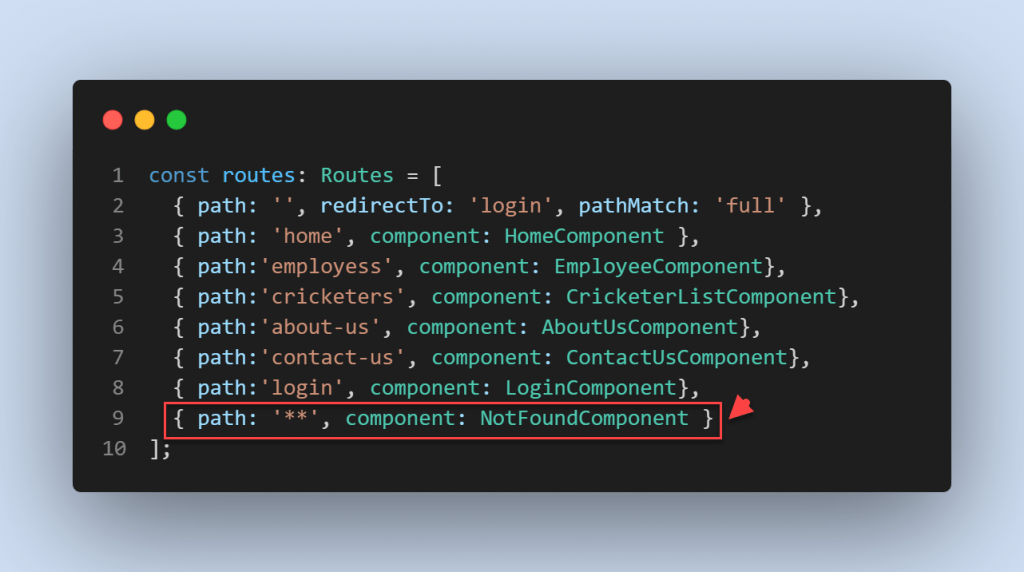
The order of the routes is very important. When matching routes find, the angular router uses first-match wins strategy. So more specific routes should be placed above less specific routes. So, Routes with a static path should be placed first, followed by the empty path route, that matches the default route. The wildcard route should be the last route in your router configuration like below,
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'home', component: HomeComponent },
{ path:'employess', component: EmployeeComponent},
{ path:'cricketers', component: CricketerListComponent},
{ path:'about-us', component: AboutUsComponent},
{ path:'contact-us', component: ContactUsComponent},
{ path:'login', component: LoginComponent},
{ path: '', redirectTo: 'login', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: '**', component: NotFoundComponent }
];Conclusion
Here we discussed about Wildcard Route in Angular. A Wildcard route has a path consisting of two asterisks (**). It matches every URL, the router will select this route if it can’t match a route earlier in the configuration. A Wildcard Route can navigate to a custom component or can redirect to an existing route.
Leave behind your valuable queries and suggestions in the comment section below. Also, if you think this article helps you, do not forget to share this with your developer community. Happy Coding 🙂
Related Articles
- Create a responsive sidebar with Angular Material- Angular 18 Example Series
- How to Deploy Angular 17/18 App in GitHub Pages
- How to convert Text To Speech With Azure Cognitive Services using Angular and .Net Core
- Angular Interceptors- The Complete Guide
- Upload Download and Delete files in Azure Blob Storage using ASP.NET Core and Angular
- Introduction to Azure Cosmos DB
- How to create Cosmos DB in Azure
- Why ReactJS is used over plain JavaScript
- Introduction to GraphQL
- Creating a Sample ReactJs Application using VS Code
Jayant Tripathy
Coder, Blogger, YouTuberA passionate developer keep focus on learning and working on new technology.
